Working in an HPC environment
Learning Objectives
- Define the basic components of a computing environment
- Explain parallelization in computing
- Log in to the FAS-RC cluster and start an interactive session
- Describe the salient features of the SLURM job scheduling system
- Describe the usage of the LMOD system
- Discuss storage options on the cluster
Clarifying some terminology
Cores
CPUs (Central Processing Units) are composed of a single or multiple cores. If I have a processor with 4 “cores”, i.e. a “quad-core” processor. This means that my processor can do 4 distinct computations at the same time.
Data Storage
Data storage is measured in bytes, usually Gigabytes (GB), Terabytes (TB), Petabytes (PB). My laptop has 1 TB of storage, which is pretty standard for laptops.
Memory
Memory is a small amount of volatile or temporary information storage. This is distinct from data storage we discussed in the previous point. It is an essential component of any computer, as this is where data is stored when some computation is being performed on it. If you have ever used R, all the objects in your environment are usually stored in memory until you save your environment. My laptop has 16 GB of memory, which is a little higher than average.
Why use the cluster or an HPC environment?
- A lot of software is designed to work with the resources on an HPC environment and is either unavailable for, or unusable on, a personal computer.
- If you are performing analysis on large data files (e.g. high-throughput sequencing data), you should work on the cluster to avoid issues with memory and to get the analysis done a lot faster with the superior processing capacity. Essentially, a cluster has:
- 100s of cores for processing!
- 100s of Gigabytes or Petabytes of storage!
- 100s of Gigabytes of memory!
Parallelization
Point #2 in the last section brings us to the idea of parallelization or parallel computing that enables us to efficiently use the resources available on the cluster.
What if we had 3 input files that we wanted to analyze? Well, we could process these files in serial, i.e. use the same core(s) over and over again, with or without multithreading, as shown in the image below.
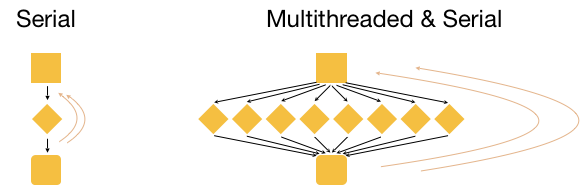
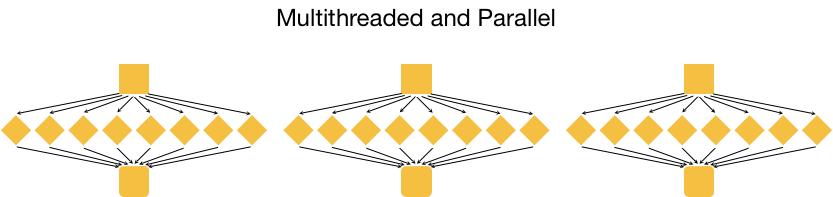
This is great, but it is not as efficient as multithreading each analysis, and using a set of 8 cores for each of the three input samples. With this type of parallelization, several samples can be analysed at the same time!
Connect to a login node on FAS-RC
FASRC accounts
For this workshop we will be using your FASRC cluster account to log in. If you do not already have a cluster account, you can request one here.
Without an existing cluster account, this workshop will provide limited value, and accounts can take some time to activate since they require approval from your PI. For this reason, we recommend having an account prior to attending this workshop.
Two-factor authentication
Access to the FASRC cluster requires two-factor authentication. Be sure that you have set-up your Duo two-factor authentication using the resources provided here.
Let’s log in
Type in the ssh command at the command prompt followed by a space, and then type your username (e.g. jharvard) plus the address of the cluster @login.rc.fas.harvard.edu. There is no space between the username and the “@” symbol (see below).
ssh username@login.rc.fas.harvard.edu
You will receive a prompt for your password, and you should type in your associated password; note that the cursor will not move as you type in your password.
After a successful password attempt, you will be queried for a “Verification code” which can be found on your Duo App. Note that the two-factor authentication used on the FASRC is different than your Harvard Key.
A warning might pop up the first time you try to connect to a remote machine, type “Yes” or “Y”.
Once logged in, you should see some news for cluster and the command prompt, e.g. [jharvard@boslogin01 ~]$.
Note 1:
sshstands for secure shell. All of the information (like your password) going between your computer and the FAS-RC login computer is encrypted when usingssh.
About nodes:
- A “node” on a cluster is essentially a computer in the cluster of computers.
- There are dedicated login nodes and compute nodes.
- A login node’s only function is to enable users to log in to a cluster, it is not meant to be used for any actual work/computing. There are only a handful of login nodes on FAS-RC.
- There are several hundred compute nodes on FAS-RC available for performing your analysis/work.
Connect to a compute node on FAS-RC
You can access compute nodes in 2 ways using a job scheduler or resource manager like Slurm.
- Directly using an interactive session (Slurm’s
salloccommand):- The
salloccommand with a few mandatory parameters will create an “interactive session” on FAS-RC. - This is essentially a way for us to do work on the compute node directly from the terminal.
- If the connectivity to the cluster is lost in the middle of a command being run that work will be lost in an interactive session.
- The
- By starting a “batch” job (Slurm’s
sbatchcommand):- The
sbatchcommand with a few mandatory parameters + a specialized shell script will result in the script being run on a compute node. - This “job” will not be accessible directly from the Terminal and will run in the background.
- Users do not need to remain connected to the cluster when such a “batch job” is running.
- The
For now let’s start an interactive session on FAS-RC using salloc.
$ salloc -p test -t 0-2:30 --mem 1G
In the above command the parameters we are using are requesting specific resources:
-p test- on the “partition” called “test” (a partition is a group of computers dedicated to certain types of jobs, interactive, long, short, high-memory, etc.)-t 0-2:30- time needed for this work: 0 days, 2 hours, 30 minutes.--mem 1G- memory needed - 1 gibibyte (GiB)
These parameters are used for
sbatchas well, but they are listed differently within the script used to submit a batch job. We will be reviewing this later in this lesson.
Make sure that your command prompt should now looks something like [jharvard@holy7c24601 ~]$.
You are now working on a compute node directly in an “interactive” session!
Let’s check how many jobs we have running currently, and what resources they are using.
$ squeue
More about SLURM
- SLURM = Simple Linux Utility for Resource Management
- Fairly allocates access to resources (computer nodes) to users for some duration of time so they can perform work
- Provides a framework for starting, executing, and monitoring batch jobs
- Manages a queue of pending jobs; ensures that no single user or core monopolizes the cluster
Requesting resources from SLURM
Below is table with some of the arguments you can specify when requesting resources from SLURM for both salloc and sbatch:
| Argument | Description / Input | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| -p | name of compute partition | test, bigmem, gpu, pi_lab |
| -t | how much time to allocate to job | 0-03:00, 5:00:00 |
| -c | max cores | 4, 8 |
| –mem | max memory | 8G, 8000 |
| -o | name of file to create with standard output | %j.out |
| -e | name of file to create with standard error | %j.err |
| -J | name of the job | Fastqc_run, rnaseq_workflow_mov10 |
| –mail-type | send an email when job starts, ends or errors out | END, ALL |
| –mail-user | send email to this address | jharvard@harvard.edu |
More detailed information for many of these arugments can be found here.
sbatch job submission script
An sbatch job submission script is essentially a normal shell script with the SLURM resource request specified at the top (SLURM directives) preceded by #SBATCH. Below is an example of an sbatch shell script that is requesting the following:
- the “shared” partition for 2 hours
- on 4 cores (30 minutes for each core)
- using 400MiB (100MiB for each core)
DO NOT RUN
#! /bin/sh
#SBATCH -p shared
#SBATCH –t 0-02:00
#SBATCH –c 4
#SBATCH --mem=400M
#SBATCH –o %j.out
#SBATCH –e %j.err
#SBATCH -J fastqc_run
#SBATCH --mail-type=ALL
#SBATCH –-mail-user=jharvard@harvard.edu
## Load the fastqc module
module load fastqc/0.11.8-fasrc01
# run fastqc (multithreaded)
fastqc -t 4 file1_1.fq file1_2.fq file2_1.fq file2_2.fq
Using software on FAS-RC
LMOD system
In the above example we want to run the FastQC tool on four files. However, before we use the fastqc command, we’ve used the command module load fastqc/0.11.8-fasrc01. This module load command is part of the LMOD system available on FAS-RC. It enables users to access software installed on FAS-RC easily, and manages every software’s dependency. The LMOD system adds directory paths of software executables and their dependencies (if any) into the $PATH variable.
So, instead of using /n/helmod/apps/centos7/Core/fastqc/0.11.8-fasrc01/fastqc as our command, we can load the module and use fastqc as the command.
Some key LMOD commands are listed below:
| LMOD command | description |
|---|---|
module spider |
List all possible modules on the cluster |
module spider modulename |
List all possible versions of that module |
module avail |
List available modules available on the cluster |
module avail string |
List available modules containing that string |
module load modulename/version |
Add the full path to the tool to $PATH (and modify other environment variables) |
module list |
List loaded modules |
module unload modulename/version |
Unload a specific module |
module purge |
Unload all loaded modules |
Exercise
- What are the contents of the
$PATHenvironment variable? - Try running the
samtoolscommand. What do you get as output? - Check if the
samtoolstool is available as a module. How many versions ofsamtoolsare available? - Load
samtools/1.10-fasrc01. Did you have to load any additional modules? - List all the modules loaded in your environment
- Try running the
samtoolscommand again. What do you get as output? - Use the
whichcommand to find out where thesamtoolstool is in the file system. - Check the contents of the
$PATHenvironment variable again. Any changes compared to before?
Filesystems on FAS-RC
- Storage on HPC systems is organized differently than on your personal machine.
- Each node on the cluster has minimal local storage; instead, most of it is on disks bundled together externally.
- Storage filesystems can be quite complex, with large spaces dedicated to a pre-defined purpose.
- Filesystems are accessed over the internal network by all the nodes on the cluster.
- There are 3 major groups on the FAS-RC cluster, each with their features and constraints:
- Shared lab storage is located in various directories, depending on your lab and the storage tier your lab may have purchased. (e.g.
/n/name_lab,/n/holylfs[02-05],/n/boslfs[02-05], etc) /home[00-15]- the home directories of all users are under these parent directories./n/holyscratch01- scratch space for temporary storage.
- Shared lab storage is located in various directories, depending on your lab and the storage tier your lab may have purchased. (e.g.
Please find more information about storage on FAS-RC by clicking here.
More about /n/holyscratch01
- It is for data only needed temporarily during analyses.
- Each user can use up to 50 TB and 1 million files/directories.
- Files older than 90 days are automatically deleted.
- No backups!
This lesson has been developed by members of the teaching team at the Harvard Chan Bioinformatics Core (HBC). These are open access materials distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution license (CC BY 4.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.